It's much more important that you get sleep than force yourself to do all these questions. Skimming many of these to see if you can come up with a viable way to start them, and actually trying a few of them more seriously would be more valuable than trying to do them all in detail!!!
Question 1
Explain how to solve the following problem using a shortest-path algorithm: The input is a two-dimensional array a[][] of floats indicating the exchange rates between currencies. So the entry a[i][j] is the amount of currency j obtained for one unit of currency i. If i corresponds to the US Dollar and j corresponds to the Canadian dollar, then a[i][j] would be about .65 and a[j][i] would be about 1/.65 or 1.55. Determine if there is a sequence of exchanges that makes money. i.e., if a[0][1] = 2, a[1][2] =2, and a[2][0] = .3, then exchanging 0's for 1's, then 1's for 2's, then 2's for 0's results in 1.2 0's for each 0 exchanged! You must describe how to set up the problem and how to solve it, including describing the algorithm you use to solve it.
Question 2
Write a method that takes as input a binary search tree, T, and two keys k1 and k2, which are ordered so that k1 <= k2, and prints all elements X in the tree such that k1 <= key(X) <= k2. You may assume that the keys are of type Comparable. Your program should run in time O(K + log N), where K is the number of keys printed.
Question 3
A min-max heap is a data structure that supports both deleteMin and deleteMax in O(log N) per operation. The structure is identical to a binary heap, but the heap-order property is that for any node, X, at even depth, the element stored at X is smaller than the parent but larger then the grandparent (where this makes sense), and for any node X at odd depth, the element stored at X is larger than the parent but smaller than the grandparent. I.e., looking at elements at odd depth only, the elements decrease as you go down the tree, and looking at elements at even depth only, the elements increase as you go down the tree.
a. Give an algorithm to find the minimum element of the tree.
b. Give an algorithm to find the maximum element of the tree.
c. Give an algorithm to insert a new node into the min-max heap.
Question 4
Give a recursive algorithm for making change with the smallest number of coins. The input to your method is an integer array coins[] containing the possible values for the coins, and an int amount indicating the amount of change needed. The output should be an array indicating the number of each coin needed. So, if the input is coins[] = {1, 5, 10, 25} and amount = 55, then the output should be an array change[] = {0, 1, 0, 2}. Hint: For the recursive step, subtract the amount of one coin from the amount of change needed. Be careful to use the smallest number of coins in your solution.
Question 5
Show the steps in finding the maximum flow in the following network:
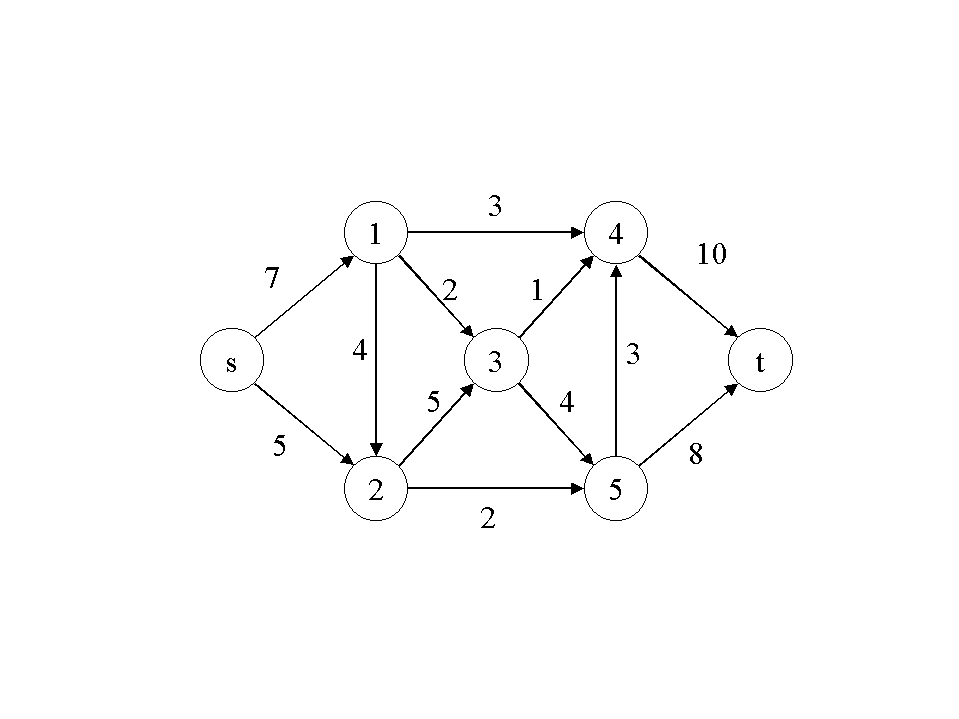
Question 6
Below is a java method with no comments and cryptic names. Describe what the method does, and give the name of the algorithm if it is one that we've studied in class.
public static void something(float a[]) { for (int b=a.length; b > 0; b/=2) { for (int i=b; i < a.length; i++) { float d = a[i]; int j = i; while (j > =b && d < a[j-b]) { a[j] = a[j-b]; j -= b; } a[j] = d; } } }
The following are from the Weiss textbook Question 7
- Write a recursive method which returns the number of 1's in the binary representation of N. (Think about how many 1's there might be in N/2.)
- Give an induction proof that ... the sum from i=1 to N of (2i - 1) equals N^2.
- Give an induction proof that ... the sum from i=1 to N of i^3 equals the square of the sum from i=1 to N of i.
Question 8
- Suppose f(x) is the polynomial a[0] + (a[1] * x) + (a[2] * x^2) + ... + (a[N] * x^N), and consider the algorithm given by ... poly = 0; for( i=n; i>=0; i-- ) poly = x*poly + a[i]; Explain why this works, and estimate its running time.
- Suppose you're given an N by N matrix of numbers in which each row increases from left to right and each column increases from top to bottom. Give an O(N) worst-case algorithm which decides if a given number X is laready in the matrix.
Question 9
- A self-adjusting list differs from a regular list in that all insertions are performed at the front, and that whenever an element is accessed by 'find' it's moved to the front of the list without changing the order of the other elements. Write array and linked list implementations of self-adjusting lists. If each element a_i has a fixed probability p_i of being accessed by 'find', show that the elements with highest access probabilties are expected to be close to the front.
- Build a data structure which supports the stack 'push' and 'pop' operations as well as a third operation 'findMin' which returns the smallest element in the data structure. All three operations must be in O(1) worst time. Show that adding a fourth operation 'deleteMin' forces at least on of the operations to take Omega(log N) time.
Question 10
- In a non-empty binary tree, a 'full node' has two non-null children. Prove that the number of 'full nodes' is one less than the number of leaves.
- Since a BST with N nodes has N+1 null references, half the space allocated for link information is wasted. Suppose that we change things so that if a left child is null, the parent's 'left' points to its inorder predecessor, and for a null right child the parent's 'right' points to its inorder successor. Call these modified links 'threads'. How can we distinguish 'threads' from 'real' child links? Write insertion and deletion methods for threaded tress. What advantages does a threaded tree have in use?
Question 11
- Describe carefully (and briefly!) the differences between linear probing, quadratic probing, and double hashing for hash tables. (Not in notes, but in text book.)
- Give an algorithm to find all nodes in a binary heap less than some given value X. Is your algorithm of order O(K), where K is the number of nodes output?
Question 12
- Suppose you're sorting a list of comparable objects where the comparison method doesn't look at all the attributes of each object (so we can still distinguish amongst objects of 'equal value'). We say that a sorting algorithm is 'stable' if objects with equal 'sorting keys' are left in the same order (with respect to each other) they were found in the original input. Which of the sorting techniques we've considered in the course are stable?
- Give a linear time algorithm to sort N fractions, given that we know that each of their numerators and denominators are integers between 1 and N (not entirely trivial).
Question 13
- Solve the 'maximum' spanning tree problem.
- Give a linear time algorithm to find the longest path in an unweighted acyclic graph (aka tree).
- You've been given a dictionary containing five-letter words (not every five-letter string is in the dictionary!!). Give an algorithm to decide if a given dictionary word A can be transformed to another given dictionary word B by a sequence of one-letter changes. All intermediate words must be in the dictionary.